- leg pain
- toe pain
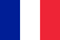
- finger pain
- swelling of big toe
- swollen ankles
- hair loss
- leg cramps
- Increased protein concentration in urine – proteinuria
- Get cold feet
- limp
- erectile dysfunction
- skin ulcers
- ulcers on feet
- Pain with significant extension and abduction of the thumb
- wrist pain
- finger pain
- forearm pain
- Deformity of fingers
- burning sensation in wrist
- Numbness in fingers - paresthesias
- swollen hands
- Stiff fingers
- Reduced finger strength
- reduced range of motion
- finger pain
- swollen fingers
- redness of skin
- Thickening of bursa
- There is a layer of white moss on the tongue
- toe pain
- finger pain
- Headache
- Red (bloodshot) eyes
- abnormal vaginal discharge
- chills and shivers
- swollen toes
- swollen fingers
- rash
- swollen lymph nodes
- finger pain
- Deformity of fingers
- Numbness in fingers - paresthesias
- swollen fingers
- Stiff fingers
- Reduced finger strength
- Finger joints creaking
- finger pain
- Diarrhea - Diarrhea
- Burning sensation in calf
- delayed ejaculation
- Difficulty urinating
- itchy skin
- numb toes
- Numbness in fingers - paresthesias
- Numbness in the hands - paresthesia
- Loss of bowel control
- loss of sensation in the legs
- loss of sensation in hands
- Stiff fingers
- leg cramps
- Rapid heartbeat - tachycardia
- Get cold feet
- limp
- chronic constipation
- Excessive sweating – hyperhidrosis
- finger pain
- Skin inflammation – eczema
- thinning of skin
- brittle hair and nails
- redness of skin
- dry skin
- pain in one arm
- finger pain
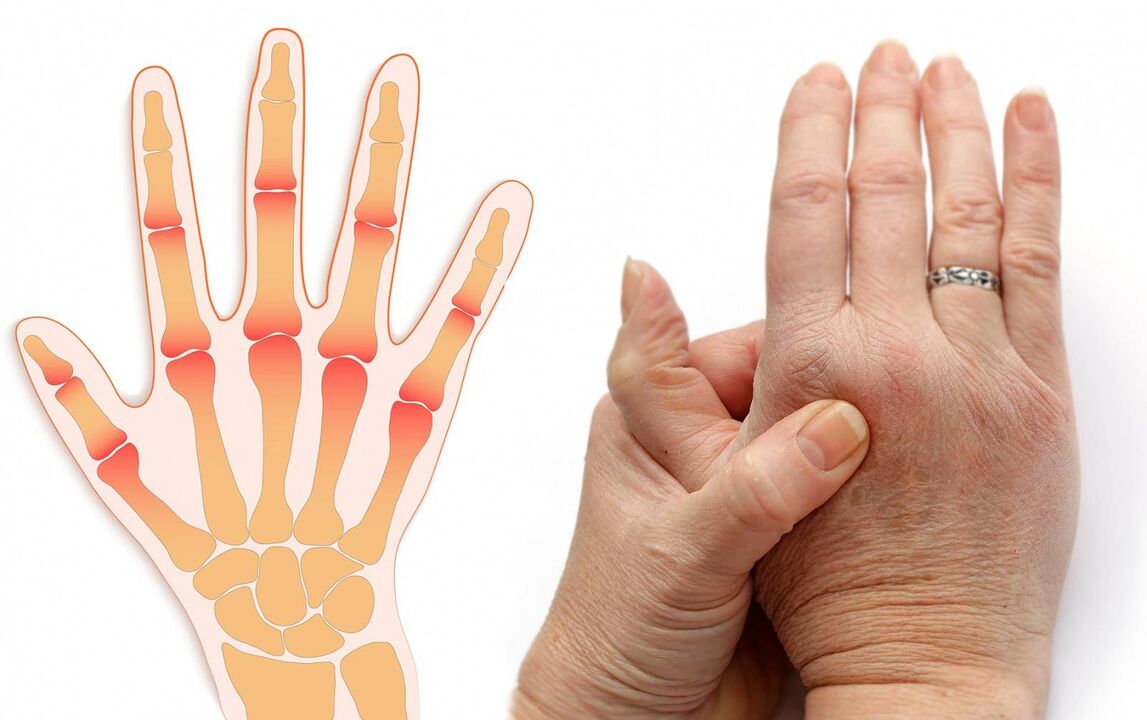
- Hand Pain
- Deformity of fingers
- muscle weakness
- swollen fingers
- Stiff fingers
- hand weakness
- lump or lump
- wrist pain
- Hand Pain
- elbow pain
- finger pain
- forearm pain
- Hand Pain
- Limited wrist movement
- Limited hand movement
- swollen hands
- loss of sensation in hands
- Stiffness in hands
- finger pain
- wrinkles on skin
- Skin inflammation – eczema
- thinning of skin
- brittle hair and nails
- finger pain
- Hand Pain
- Pustules
- Deformity of fingers
- itchy skin
- brittle hair and nails
- finger pain
- Bones protruding from the skin
- swollen fingers
- redness of skin
- Stiff fingers
- wrist pain
- Hand Pain
- finger pain
- Limited wrist movement
- Limited hand movement
- swollen hands
- Stiffness in hands
- Pain with significant extension and abduction of the thumb
- finger pain
- Deformity of fingers
- Curvature of little finger and ring finger
- Numbness in fingers - paresthesias
- swollen fingers
- Stiff fingers
- Finger joints creaking
- wrist pain
- Hand Pain
- finger pain
- Limited wrist movement
- Limited hand movement
- swollen hands
- Stiffness in hands
- Hand Pain
- finger pain
- high temperature - high fever
- Deformity of fingers
- chills and shivers
- swollen fingers
- Loss of appetite
- Problems with grasping objects with hands
- Stiffness in hands
- Stiff fingers
- Reduced finger strength
- chest pain
- Bone pain (bone pain)
- finger pain
- arthralgia - joint pain
- "Sausage" finger inflammation
- Stunting
- iron deficiency anemia
- swelling of the legs
- swollen fingers
- swollen hands
- Yellowing of the skin and pupils - jaundice
- Losing consciousness - fainting
- decreased vision
- Rapid heartbeat - tachycardia
- Chronic fatigue - increased fatigue
- finger pain
- Hand Pain
- Shortness of breath - difficulty breathing
- Numbness in the hands - paresthesia
- swollen hands
If you have pain in your fingers, when should you see a doctor?
- Finger pain is severe or interferes with normal activities;
- Pain that worsens at night;
- Pain did not subside after a week of at-home treatment;
- Tingling or loss of sensation in the hands;
- Have a history of diabetes;
- Inability to move thumb or hold objects;
- Changes in the shape or color of the phalanges.
diagnosis
- Stool analysis for the presence of dysbiosis
- blood analysis
- Vitamin D test
- Arthroscopy
- Biopsy
- skin biopsy
- lymph node biopsy
- blood chemistry
- bronchoscopy
- Dermoscopy
- Dual-sided scanning of lower limbs
- Immunology research
- Polymerase Chain Reaction Test
- Finkelstein Study
- Ehoff's research
- Skin test
- computed angiography
- Lower extremity computed angiography
- Chest computed tomography
- Computed tomography of hand
- lung computed tomography scan
- lymph node computed tomography
- wrist computed tomography
- Neck vascular computed tomography
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the hand
- lymph node magnetic resonance imaging
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist
- cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
- MRI of joints
- Smear microscopy
- radiography
- Chest X-ray
- Hand X-ray
- Chest X-ray
- Wrist X-ray
- X-ray examination of lower limbs
- X-ray of finger
- Finger radiography
- Esophageal X-ray
- Serological testing
- thoracentesis
- abdominal ultrasound
- Upper limb venous ultrasound
- Brain Ultrasound - Neurosonography
- Hand ultrasound
- Ultrasound examination of wrist joint
- Ultrasound examination of soft tissues of the hand and arm
- Spleen ultrasound
- Heart Ultrasound - Echocardiography
- Chest X-ray
- Neuroelectromyography
How to relieve finger pain?
- Apply ice for 20 minutes every 2-3 hours;
- painkiller;
- Stop or reduce activities that cause pain, such as typing, working with vibrating tools, or playing a musical instrument;
- Do not take hot baths, go to saunas or bathhouses for 2-3 days after the injury;
- Don't lift heavy objects.